Sustainable Farm
Introduction
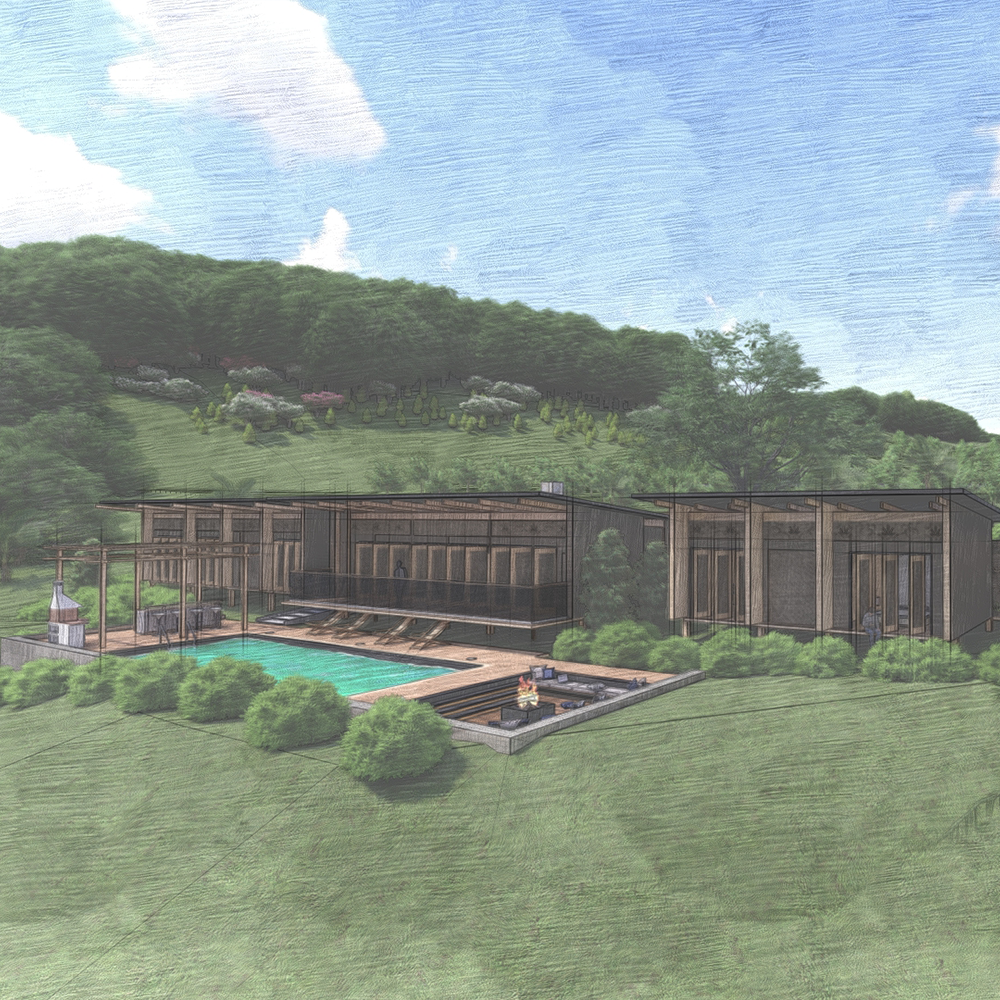
The proposed sustainable farm project embodies a holistic approach to environmental stewardship and energy efficiency. By leveraging solar power, innovative water management systems, and natural ventilation techniques, the project aims to minimize its ecological footprint while maximizing comfort and utility for its inhabitants.
Energy Management
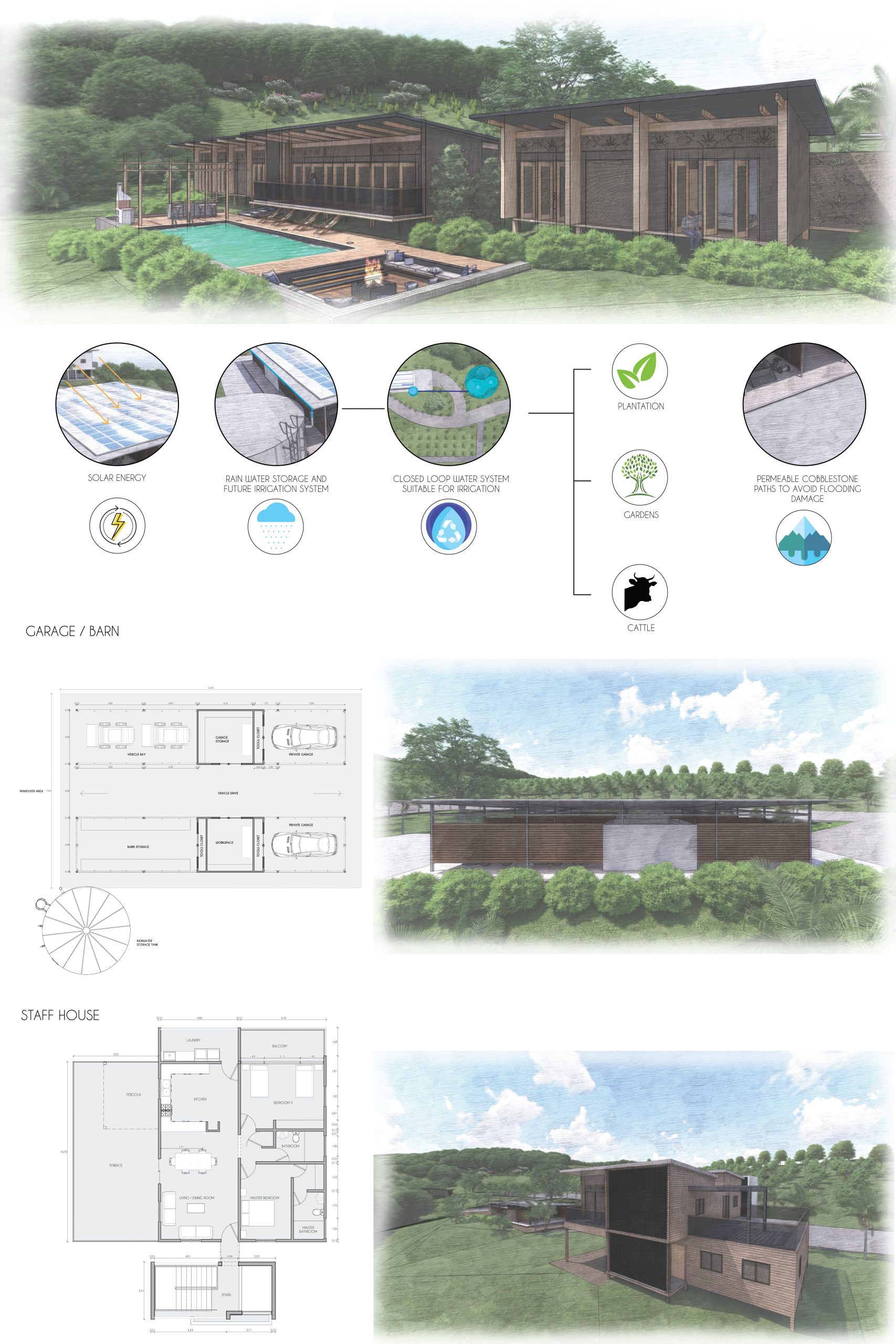
Central to the project’s sustainability is the use of solar panels. These panels harness solar energy to supply all the electrical needs of the farm. This renewable energy source not only reduces reliance on fossil fuels but also ensures a steady supply of clean energy. The integration of solar energy highlights the commitment to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting energy independence.
Water Management
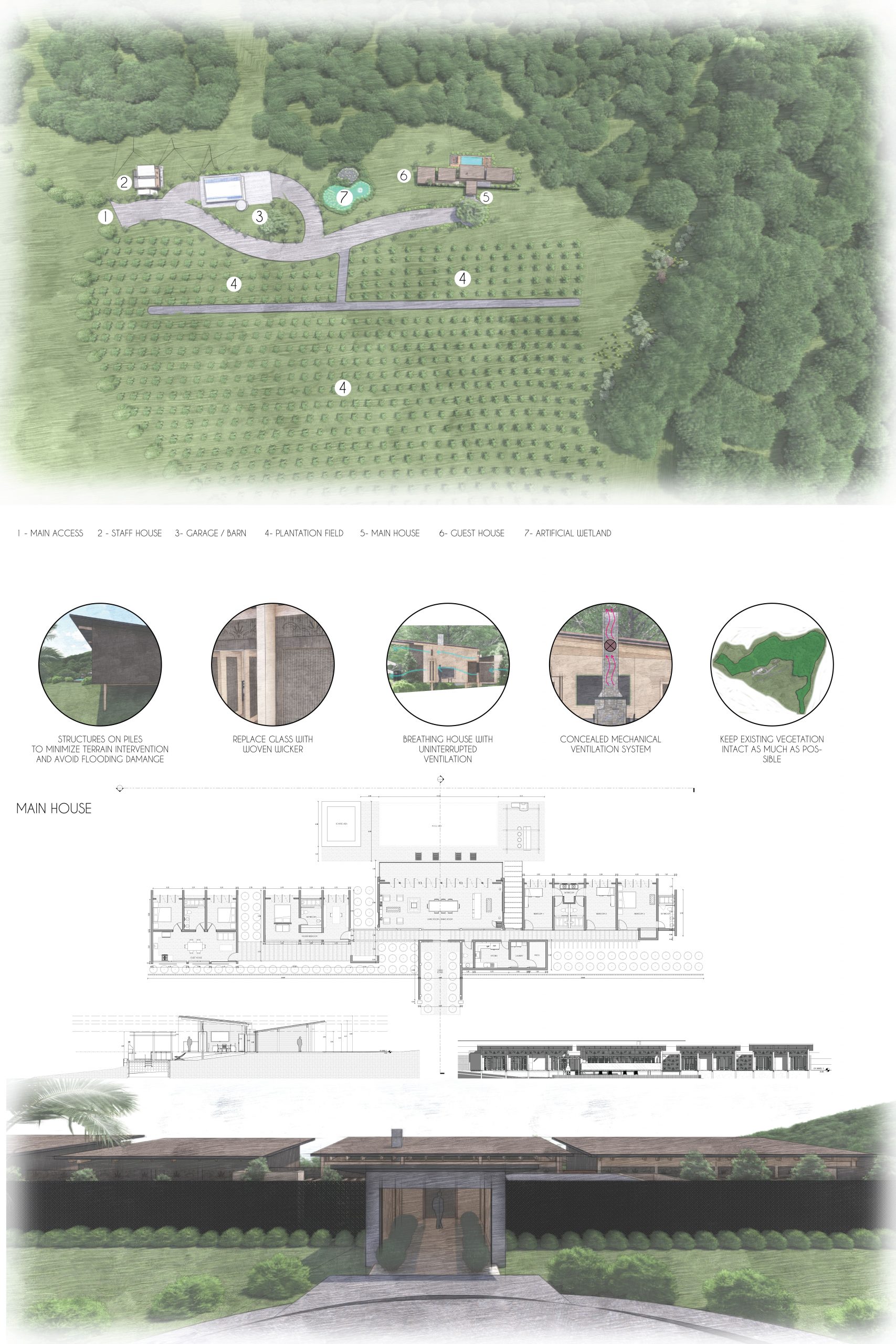
Water sustainability is addressed through the implementation of artificial wetlands and rainwater harvesting systems. The artificial wetlands are designed to treat wastewater and rainwater, making it suitable for irrigation, and supplying clean water for non-potable uses such as flushing toilets, washing vehicles, and cleaning the house. This closed-loop water system ensures that water resources are efficiently used and recycled, significantly reducing the demand for fresh water and mitigating the impact on local water sources.
Architectural Design
- Woven Wicker Windows: Unlike conventional glass windows, woven wicker windows are used to enhance natural ventilation and prevent heat retention. This design choice ensures a cooler interior environment and promotes airflow throughout the house.
- Single-Pitched Roof: The roof is designed to align with the wind direction, creating a breathing house with uninterrupted ventilation. This architectural feature not only facilitates natural cooling but also reduces the need for mechanical cooling systems.
- Structures on Piles: To minimize terrain intervention and reduce the transfer of ground heat to the building, the structures are elevated on piles. This approach also protects the buildings from potential flooding and allows for better air circulation underneath the structures.
- Concealed Mechanical Ventilation: A concealed mechanical ventilation system is integrated to extract hot air trapped inside the house, ensuring a consistent flow of fresh air and maintaining comfortable indoor temperatures.
- Openwork Blocks: The use of openwork blocks in the construction provides ventilation while maintaining privacy. These blocks allow air to flow freely, enhancing natural cooling and reducing the reliance on artificial ventilation.